Here’s everything you need to know before investing in ETF (Exhange Traded Fund). This is your complete ETF guide as a beginner planning to invest in an ETF.
So, you have started investing in the stock market, and you stumbled upon another type of investment, an ETF. Perhaps, you heard a fellow investor talking about his latest ETF from his portfolio. Now you want to learn more about what an ETF is and how to invest in one.
What is an ETF?
An ETF is an acronym of Exchange-Traded Fund. It is an investment fund or a basket of investments (including stocks, bonds, and other securities) traded on stock exchanges.
There are different kinds of exchange-traded funds aiming for different investment objectives. Some ETFs invest in numerous stocks and bonds, while some track a specific sector like the 5G technology or renewable energy sectors.
Some ETFs track a particular stock index’s performance such as the S&P 500 index or the NASDAQ 100 index. On the other hand, some ETFs track the inverse performance of a specific stock market index.

ETF vs. Stocks
The difference between an ETF compared to a stock is share ownership. When you buy a stock, you own a share of a particular company but when you buy an ETF, you own a share of pooled investments because an ETF is a basket of different assets such as bonds, stocks, and other securities, all pooled to form one fund, the ETF.
ETF vs. Mutual Funds
What is the difference between an ETF and a mutual fund? They are both professionally managed investment funds and pooled funds. The main difference between ETFs compared to mutual funds is the way they are available to trade. ETF can be traded like stocks, but mutual funds are only traded at the end of the day.
ETF vs. Index Funds
The differences between an index fund compared to an ETF are usually the fees and way of trading. Index Fund is a type of mutual fund that copies the performance of a specific stock market index (like S&P 500, Nasdaq 100 index, etc.).
Index funds prices are based on the NAVPS (Net Asset Value Per Share). They are also traded at the end of the day.
Index funds can also be invested automatically through a broker without paying additional fees. If you want to invest in an ETF periodically, you need to buy your ETF shares through your trading platform. Doing so will charge you some trading fees or commission fees.
Advantages of Investing in ETF:
To earn passive income
There are two ways you can earn money when you invest in an Exchange-Traded Fund:
Growing Value of your ETF
As your ETF price per share increases, your investment also grows in value. It is important to know your objective and goals to decide how you can achieve your target profit. While ETFs can be traded like stocks, they can also be risky to trade like stocks.
Dividends
Many ETFs pay dividends to their investors as a payout of part of the fund’s earnings and capital gains. However, not all ETFs reward dividends. Some ETFs choose to reinvest their profits into their holding companies.
ETF provides diversification
One of the benefits and advantages of investing in ETFs is they provide diversification because your fund will be invested into numerous securities or assets. Diversification also helps reduce and balance risk.
ETFs are managed by experts
Exchange-Traded Funds are managed by asset management firms and run by financial experts and professionals. The top five biggest ETF companies in the world include iShares, Vanguard, State Street SPDR, Invesco, and Charles Schwab.
To save time in research
ETFs are managed by experts who have excellent techniques and strategies in choosing the best companies to grow the fund’s money. It can help investors who don’t have much time researching and picking growth-potential stocks.
Disadvantages of Investing in ETFs:
Volatility and Risks
Since exchange-traded funds are traded in the stock market, their prices fluctuate and swing like stocks. Economic, geopolitical, and global market factors can affect the movement of ETFs. Additionally, some sectors are more volatile than others.
Therefore, investors must be aware of what types of investments the ETF allocates its funds, what benchmark it is following, and whether the positions are leveraged.
Expense Ratio
Since ETFs are managed by experts, they are attached with an expense ratio representing all the expenses, such as the management fees and operating costs of the ETF. This expense ratio is already taken out of the underlying net asset value of the exchange-traded fund.
Trading Fees
We now know that ETFs can be traded like stocks. That also means investors will need to pay a commission or trading fee every time they buy or sell an ETF. A trader must also consider spreads and fees, especially when trading with leverage.
How to Invest in an ETF online?
Step 1: Open a legit broker account
If you want to invest in most of the best performing ETFs in the world using one trading platforms like Robinhood and Webull (verify first if these apps are accredited in your country). Some brokers offer lower minimum fund to invest in ETF, stocks, and other assets. They are also user-friendly. Investors can monitor every ETF trade position they hold in a nifty way.
Note that some retail investor accounts lose money when trading stocks and ETFs. You should consider whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Step 2: Find an ETF that suits your investment objective
Every ETF is different, just like every investor is different. It is essential that you choose the best ETF suitable for your interest, risk profile, investment horizon, and objective.
There are numerous kinds of exchange-traded funds available for every investor. Check out their prospectus, fund fact sheet, historical performance, and holdings. Make sure they match your objectives and goals.
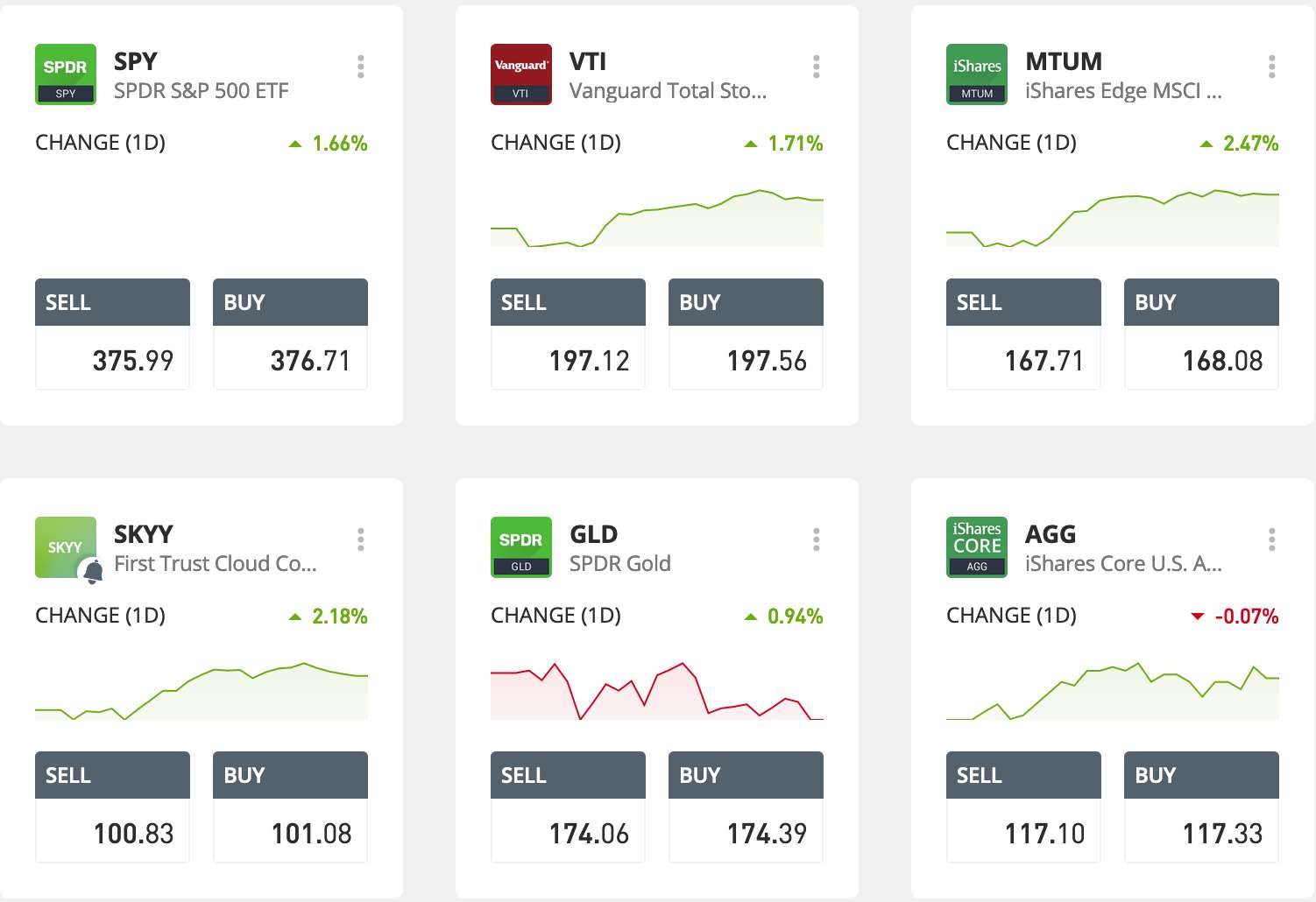
ETF Examples:
- SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) – tracks the performance of the S&P 500 index
- Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) – holds over 3,800 individual US equities including large, mid, and small-cap companies
- Invesco S&P 500 High Dividend Low Volatility ETF (SPHD) – mirrors the investment results of the S&P 500 Low Volatility High Dividend Index
- iShares Core US Aggregate Bond ETF (AGG) – composed of the total US investment-grade bond market
- Invesco Solar ETF (TAN) – composed of companies in the solar energy sector
Step 3: Buy your chosen ETF
Now that you’re ready and you have chosen the best ETF suitable for you, you can start buying some shares of your ETF. Log in to your trading platform and execute a BUY order.
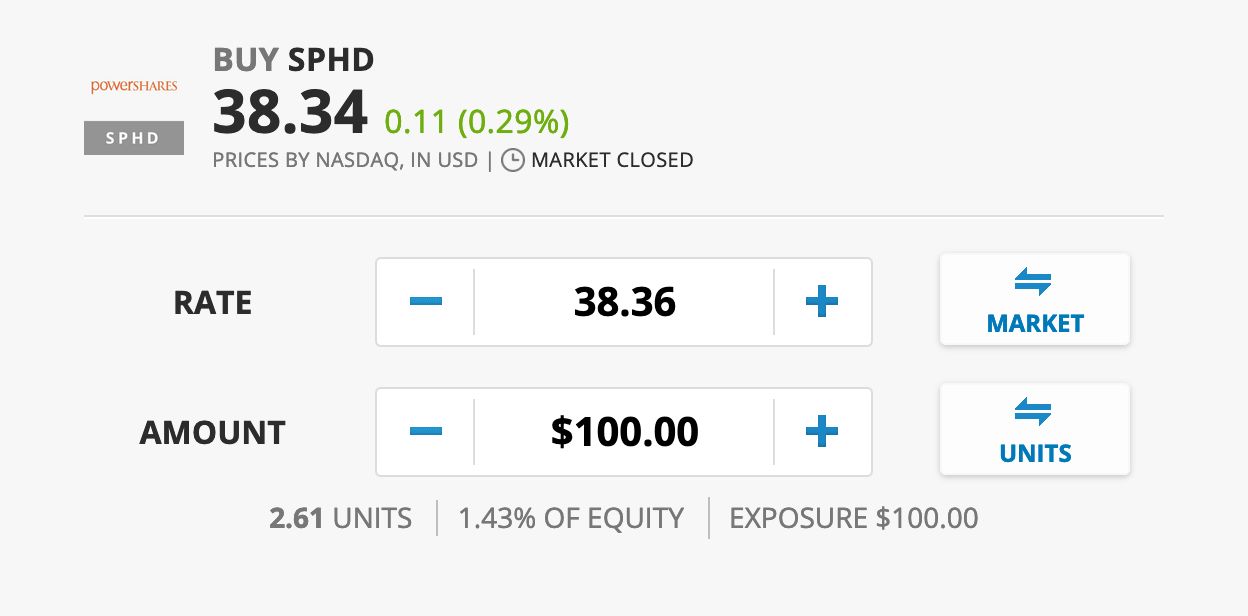
Step 4: Follow your Target Profit
Set your Target Profit or Target Price if you want to automatically lock in your profit when the ETF’s price hits your target. Otherwise, leave the TP option untouched if you prefer to set it later.
MORE ETF TUTORIALS HERE: Latest ETF Guides
Disclaimer: This article is for information purposes only and should not be considered as a professional advice or endorsement of a particular investment. All investments have risks. Risk only the capital you’re not afraid to lose. Always do your own research before investing.



